The most direct definition of lodging properties is the one provided under the Building Act. The Building Act classifies buildings by use into 30 categories, and “lodging properties” are one of them. A building’s use classification—i.e., the category of building use—is a factor that determines what types of buildings may be constructed on a given parcel. For example, if a parcel is designated as a “residential zone,” it is highly likely that a “lodging property” will not be permitted.
In Korea, the law most broadly applicable to the lodging business is the Public Health Control Act, which applies to the general and residential lodging properties operation. The facility standards for hotels and resort condos that qualify as tourist lodging properties are governed by the provisions of the Tourism Promotion Act. In general, the standards are primarily centered on the number of guest rooms and the types and scale of ancillary facilities.
In the narrow sense, lodging properties must meet the following requirements according to ‘Enforcement Regulation of Public Health Control Act, Annex 1’:
- Residential lodging properties must have cooking facilities and ventilation facilities or windows. If cooking facilities are installed indoors, fixed cooking facilities must be installed in each room or in a communal cooking area.
- Residential lodging properties must have a bathroom or shower in each room. However, a “hostel”, as defined in Article 2, Paragraph 1, Subparagraph 2(m) of the Enforcement Decree of Tourism Promotion Act, may have shared bathrooms or showers.
- For lodging properties that are part of a building, the guestrooms must either occupy dedicated floors or have 30 or more rooms, or the area used for lodging business must be at least one-third of the building’s gross floor area. However, considering regional conditions, the number of rooms and area standards may be relieved by ordinances of metropolitan cities, provinces, special self-governing cities, or special self-governing provinces.
Meanwhile, under the KSIC, there are subcategories of the lodging business that use buildings designated for purposes other than lodging properties under the Building Act. Representative examples include minbak businesses and campsite businesses. Minbak businesses use single-family houses or multi-family housing under the Building Act, while campsite businesses use campsite facilities as defined under the Building Act.
Furthermore, regarding the dormitory and gosiwon operation—which are classified as the other lodging business rather than the general and residential lodging property operation under the KSIC—the standards stipulated in the Public Health Control Act, the Tourism Promotion Act, and the Agricultural and Fishing Villages Improvement Act do not apply. In addition, facilities such as youth training centers or accommodations within natural recreation forests, while not technically classified as lodging businesses under the KSIC, operate in a similar manner and can therefore be considered lodging properties in a broader sense.
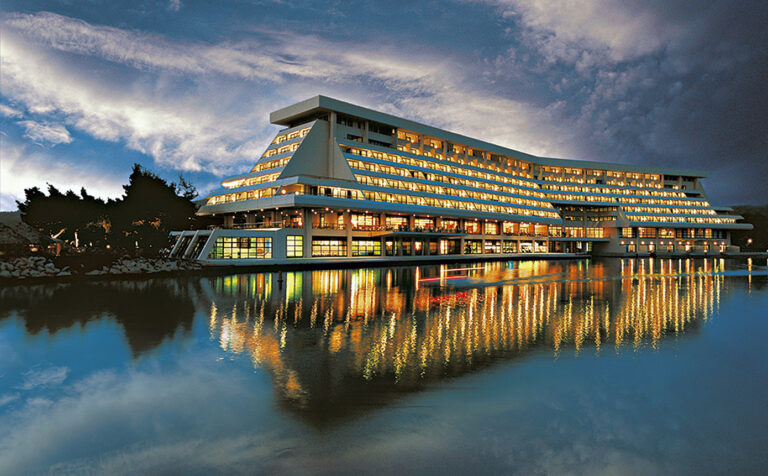
In a broad sense, lodging properties generally consist of the following three parts:
- Guestrooms: Guestrooms are spaces for sleeping and are the most essential part of a lodging property. While some lodging properties might lack other parts, none can exist without guestrooms. Additionally, the quality of guestrooms is the most significant factor influencing the pricing of lodging products.
- Amenities: Spaces where optional services are provided, other than sleeping, are called amenities. For example, food and beverage outlets, lounges, banquet halls, swimming pools, and casinos fall under amenities. Depending on the type of lodging property, the relevant laws may specify the requirements for amenities.
- Public Facilities: Public facilities do not directly generate revenue, but without them, the establishment cannot fulfill its role as a standalone product. The lobby is an example of public facilities. Other public facilities include parking lots, staff spaces, mechanical rooms, electrical rooms, and linen rooms.