The contents are in progress.
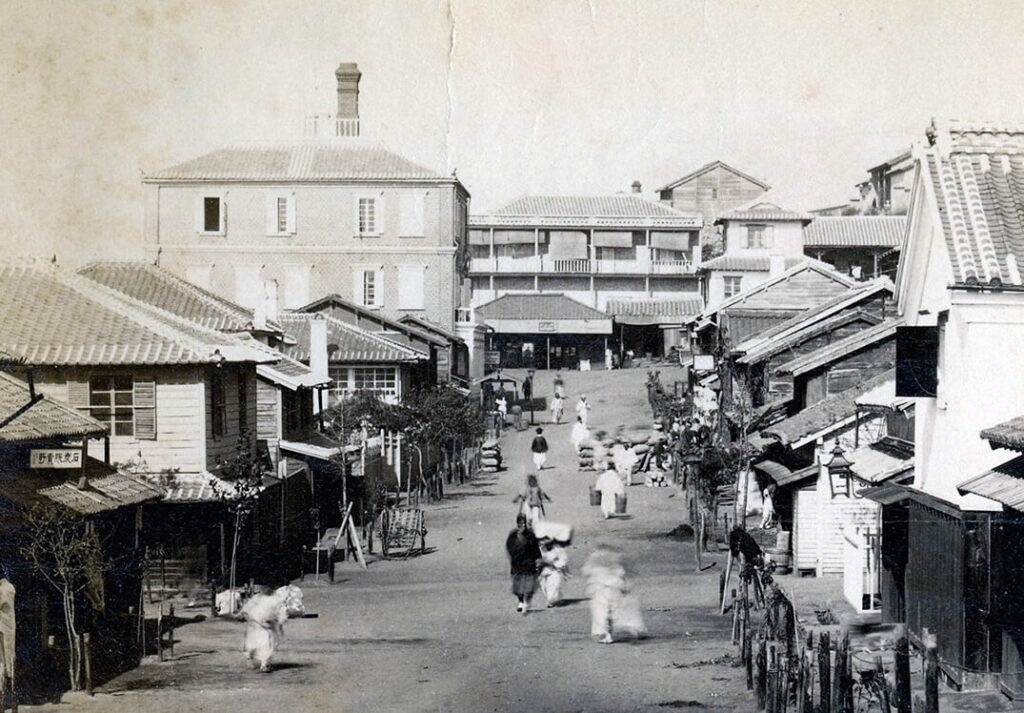

Japanese Hisataro Hori and his son Rikitaro Hori opened an 11-room Daebul Hotel in 1888 at Jogyeji (now Chinatown) near Incheon Port and operated it for Westerners entering and leaving Seoul. With the opening of the Gyeongin Line in 1899, accommodation in Incheon was no longer needed, and the Daebul Hotel was converted to a Chinese restaurant which ended up demolished in 1978.
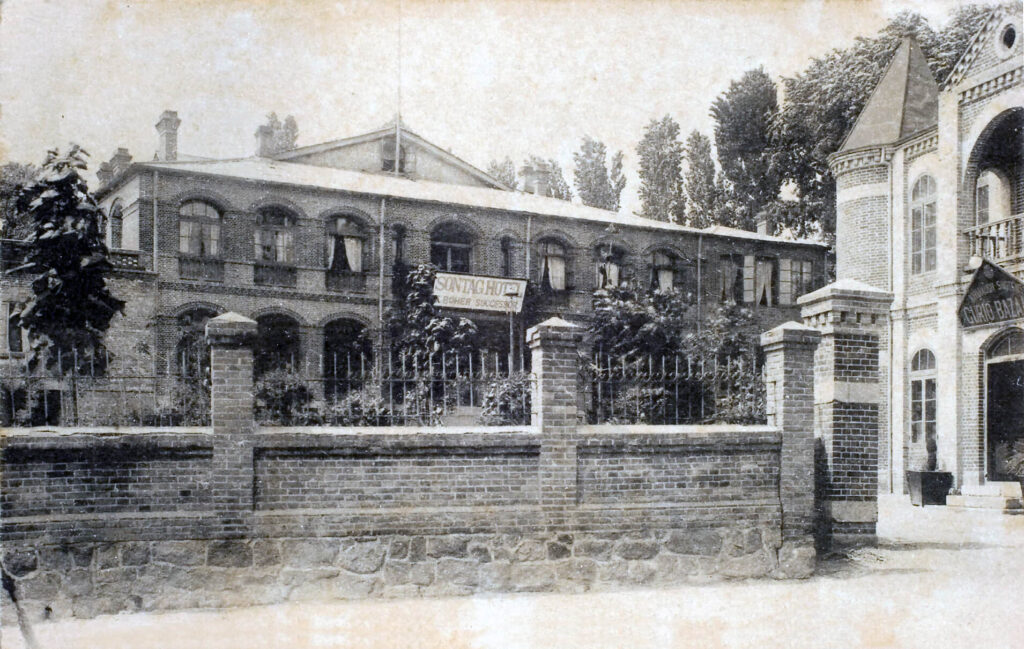

In 1902, Emperor Gojong built a 25-room hotel near Deoksugung Palace, currently the site of the 100th Anniversary Memorial Hall of Ewha Girls' High School, and granted it to a French ritualist Mrs. Antoinette Sontag. The Sontag Hotel began to suffer from financial difficulties after Mrs. Sontag left Korea in 1909, which ended up closed down in 1917 with the opening of Chosun Hotel.
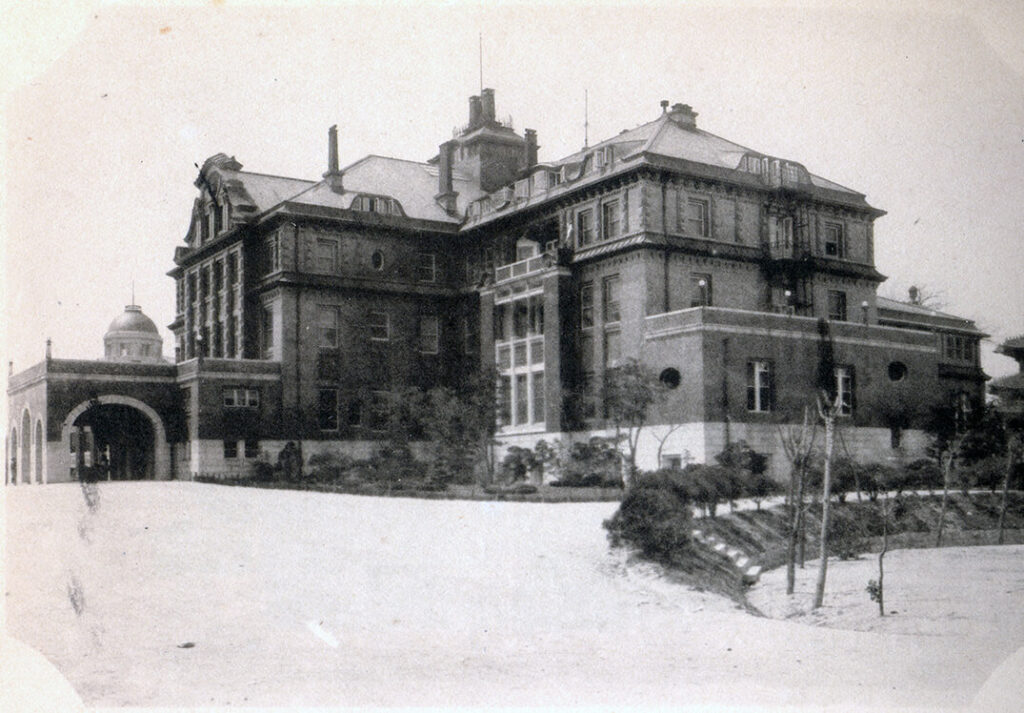

The first Chosun Hotel was built with 64 rooms in Sogong-dong, where Hwangudan was located, by the Railway Bureau of the Japanese Government-General of Korea. After liberation, it was used as the US Military Command, and the government of Korea took it over upon establishment of the government. It was used as a temporary residence for Syngman Rhee, the first president, and during the Korean War, it was also used as a US military recreation facility.
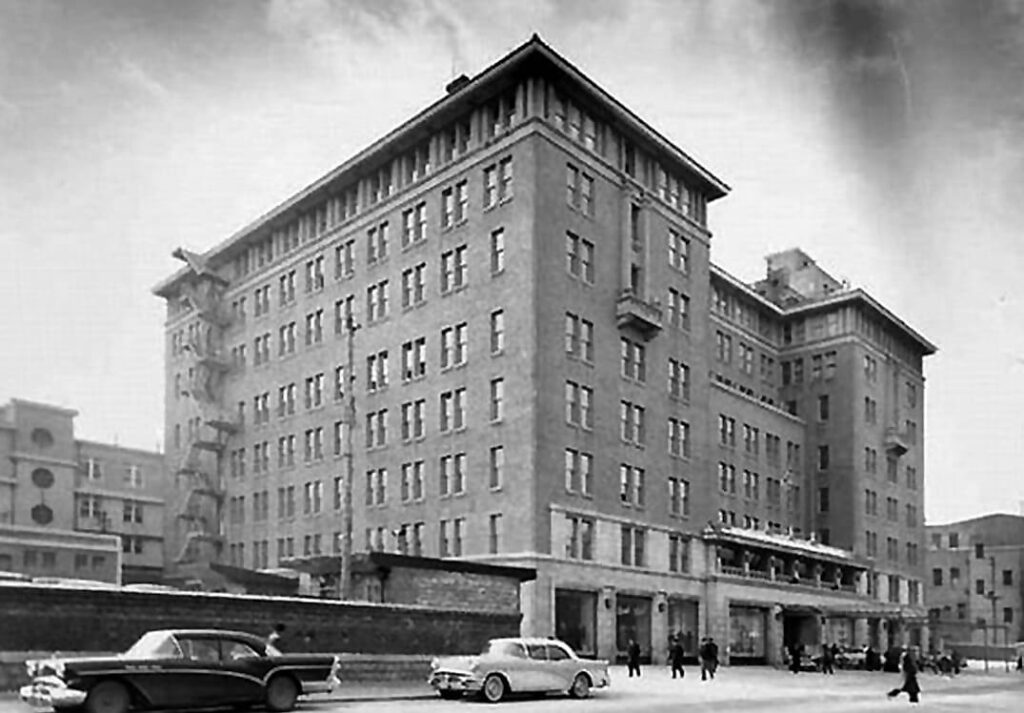

It is a 111-room hotel opened in 1938 by Sitagau Noguchi, a Japanese entrepreneur in Korea, right behind the Chosun Hotel. After he was kicked out of the Chosun Hotel due to shabby outfit, he bought a site right behind it and built a hotel twice as tall as the Chosun Hotel. It was transferred to the International Tourism Organization in 1963 with the Chosun Hotel.
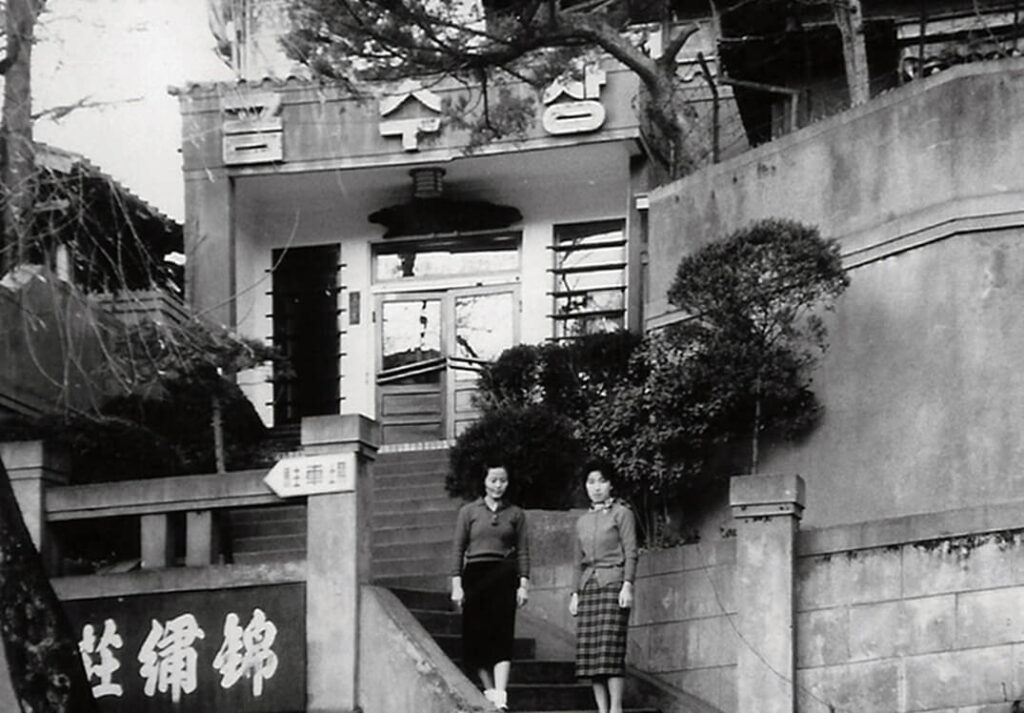

In 1955, Seo Hyun-soo, a private entrepreneur, opened a two-story 19-room Geumsujang at the current Ambassador Hotel location. It was renamed as the Ambassador Hotel in 1965, and reconstructed in 1975 to a larger hotel with 450 rooms. It entered into a strategic alliance with the global brand Accor in 1987 and has reached today, and it is the first hotel built by domestic private capital.
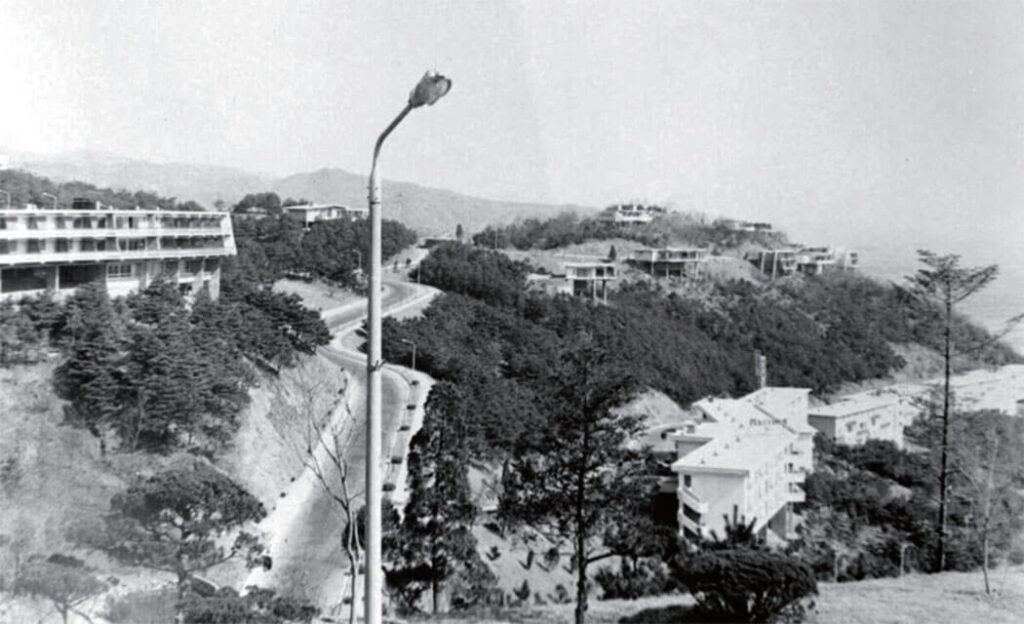

In 1961, Kim Jong-pil, the head of the Central Intelligence Agency, promoted the construction of the Walkerhill Hotel as an entertainment facility for the US military, and when the International Tourism Organization was launched, the project was transferred. In 1963, the Walkerhill Hotel was opened, consisting of 26 buildings including five guestroom towers, 13 villas, an observatory and a garage. It was the first hotel in Korea with a night club, a blowling alley and an indoor swimming pool.
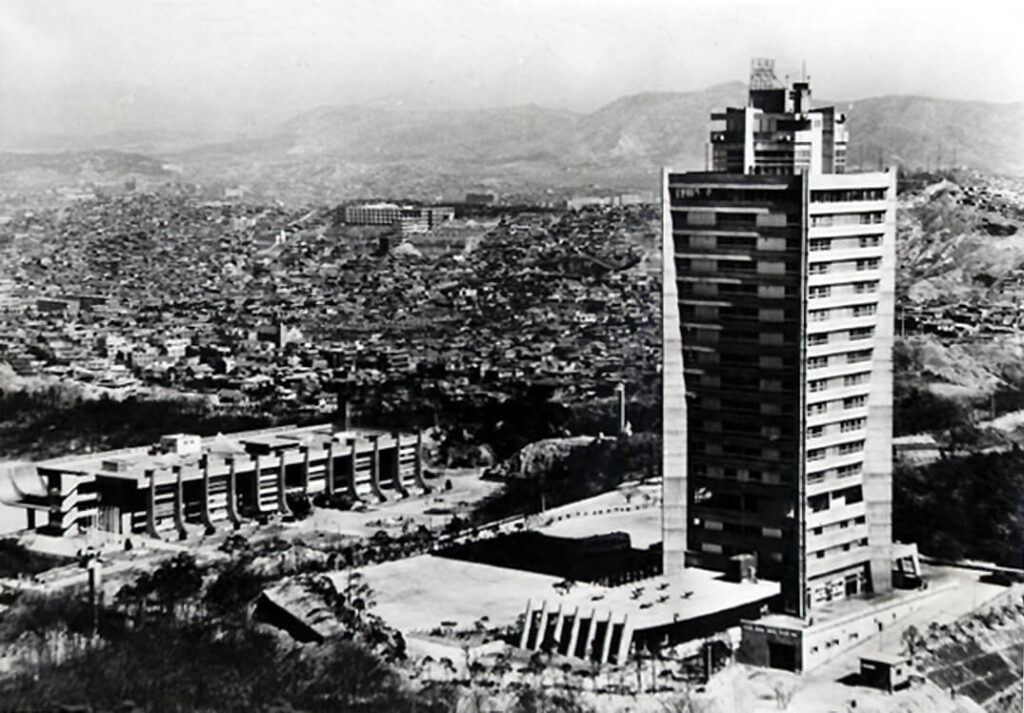

In 1964, the Freedom Center of the Asian Anti-communism Federation (now the Korea Freedom Federation) was built in Namsan. At that time, a 17-story free hall was built next to the five-story main building as an accommodation for foreign visitors. It was acquired by the International Tourism Organization in 1966 and renovated to open as the Tower Hotel in 1967, but it was sold immediately to Gongseong Industry in 1968.
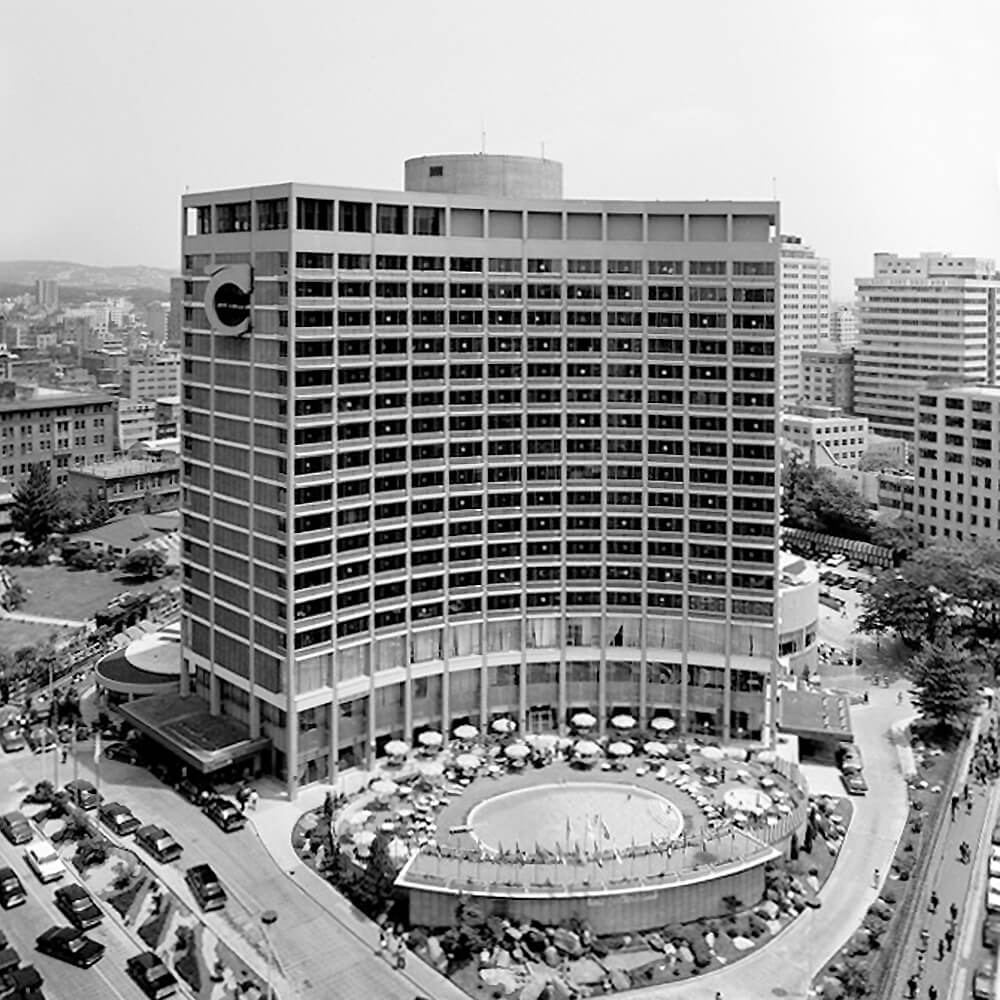

The Korea International Tourism Organization, which took over the Chosun Hotel, finally demolished it to build a new hotel, and pushed for the reconstruction of a large-scale hotel. In 1970, it opened a new 19-story 504-room Chosun Hotel in cooperation with American Airlines of the USA, and affiliated with the global brand Westin in 1981, changing the name to Westin Josun Hotel.
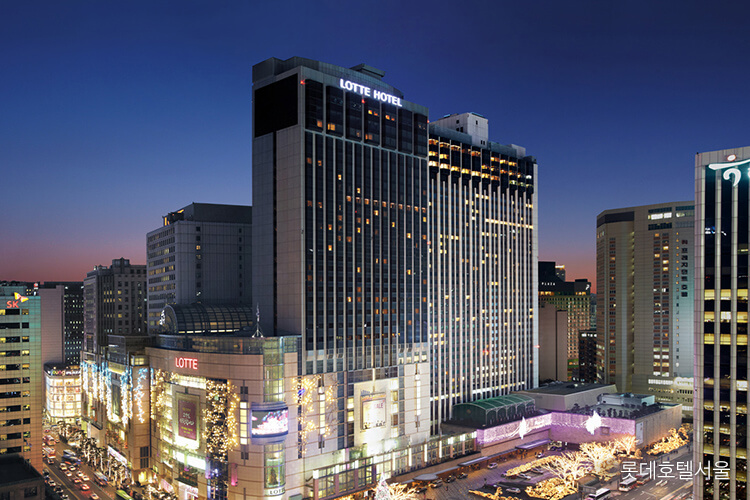

In 1973, Lotte acquired Bando Hotel from the International Tourism Organization and also acquired the site of the adjacent National Library. After demolishing the existing buildings, the 38-story Lotte Hotel main building was built in 1979. The duty-free shop was added in 1980 and the new building was added in 1988 when the Olympics were held, and is currently operating as a 1,015-room super hotel.
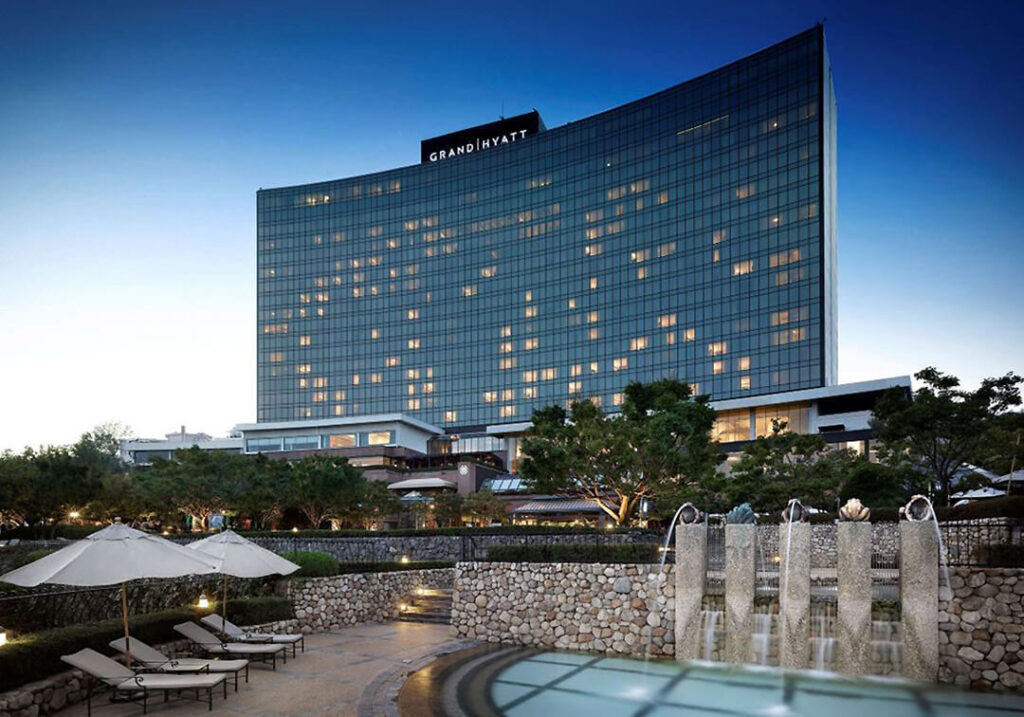

President Park Chung-hee, who attended the completion ceremony of the Namsan Foreign Apartment in 1972, ordered the construction of a hotel in Namsan, and in 1973, the Seoul Miramar Tourism Company was established in a joint venture between Korea and Japan to promote the construction of the Namsan Hotel. Opened in 1978 as a 611-room Hyatt Regency Seoul, the hotel was changed to Grand Hyatt Seoul in 1993 after extensive remodeling.
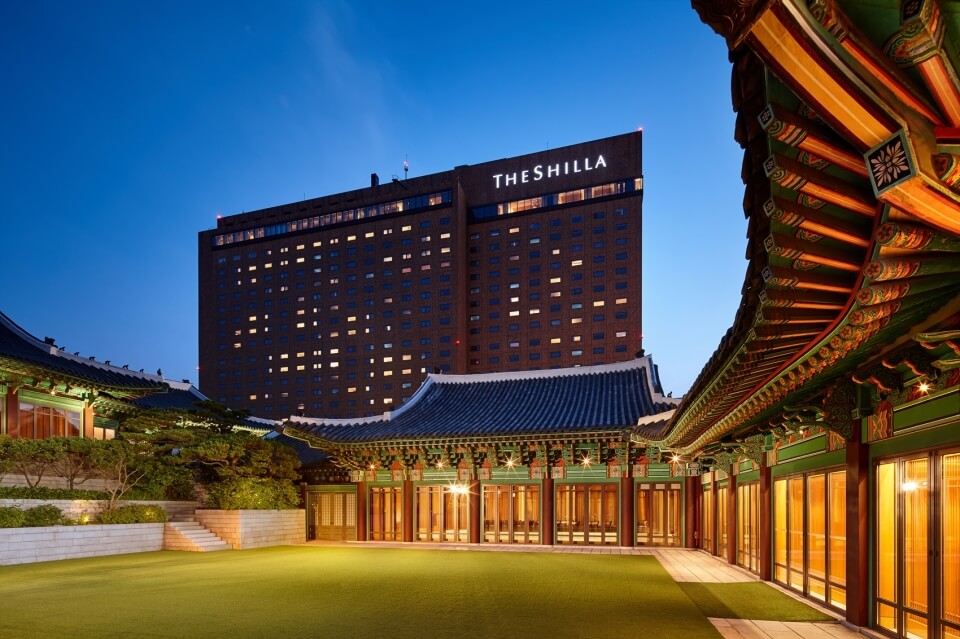

The Park Chung-hee government built the Blue House Guest House in 1967 on the site in Jangchung-dong, where a temple dedicated to Hirobumi Ito was during the Japanese occupation. However, the Blue House handed it over to Samsung in 1973 when privatizing the hotels and built a new guesthouse within the Blue House. Samsung built the 464-room Shilla Hotel in 1979 next to the guesthouse acquired.
The contents are in progress.